What is Weight Loss Surgery ?
Some people who are overweight or suffer from obesity are unable to lose weight using conventional methods. In such cases, we recommend weight-loss interventions like bariatric surgery.
Weight loss or bariatric surgery is the most effective and durable solution capable of achieving sustainable and long-lasting weight loss. It not only sheds off stubborn kilos but also helps to prevent, treat, resolve, and manage life-threatening diseases, minimize medications, and reduce the financial burden of health expenses.
In addition to treating obesity, weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric or metabolic surgery, is performed to treat and resolve diseases like diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, infertility, obstructive sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), and other obesity-related comorbidities.
Are you a Candidate for Surgery?
Before exploring treatment options (surgical or non-surgical), It is important to know your BMI because that is what defines the degree of obesity and therefore determines what type of treatment will be the most effective for you and if you are a candidate for bariatric surgery.
Read: What is bariatric surgery?
According to The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “Weight that is higher than what is considered as a healthy weight for a given height is described as overweight or obese.”
We recommend this surgery for a person who has a BMI of 27.5 or above, taking into consideration whether or not they have obesity-related complications and the level of effectiveness of non-surgical treatments they have already undertaken.
Below is the classification for BMI in Asians:
| Category | BMI |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 to 23.5 |
| Overweight | 23.6 to 27.5 |
| Obesity Class 2 (Obesity) | 27.6 to 32.5 |
| Obesity Class 2 (Serious Obesity) | 32.6 to 37.5 |
| Obesity Class 3 (Severe /Morbid Obesity) | 37.6 or higher |
To calculate your BMI, click here.
Types of Weight Loss Surgery
Weight loss (bariatric) surgery involves removing or changing a part of a person’s stomach or small intestine to minimize food consumption or absorption of calories. The surgery can either make the stomach smaller, or it can bypass part of the digestive system which helps the patient lose weight and reduce the risk of/manage/resolve high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, and other aspects of metabolic syndrome that can result from obesity.
The three main types of surgery are:
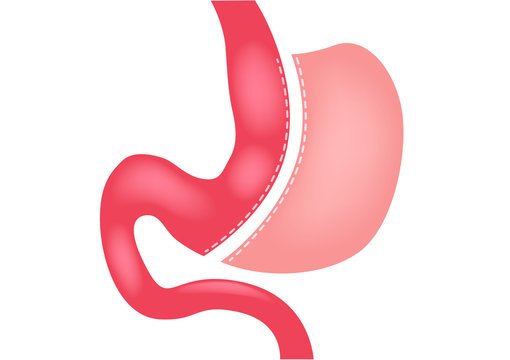
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
-
-
-
- Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy is the most common Weight Loss Surgery performed all over the world (more than 60%).
- This is an irreversible operation with the lowest rate of complications.
- Almost 80% of the stomach is removed and the remaining portion looks like a ‘sleeve’, which is the “new” stomach.
- The secretion of the hunger hormone ‘ghrelin’ is significantly reduced which results in decreased appetite and early satiety, minimizing food consumption.
- There is rapid weight loss and remission of diseases post-surgery.
- This procedure is not recommended in patients with a sweet tooth and acid reflux disease (GERD, reverse flow of food content, and acid from the stomach to feeding tube i.e. oesophagus).
-
-
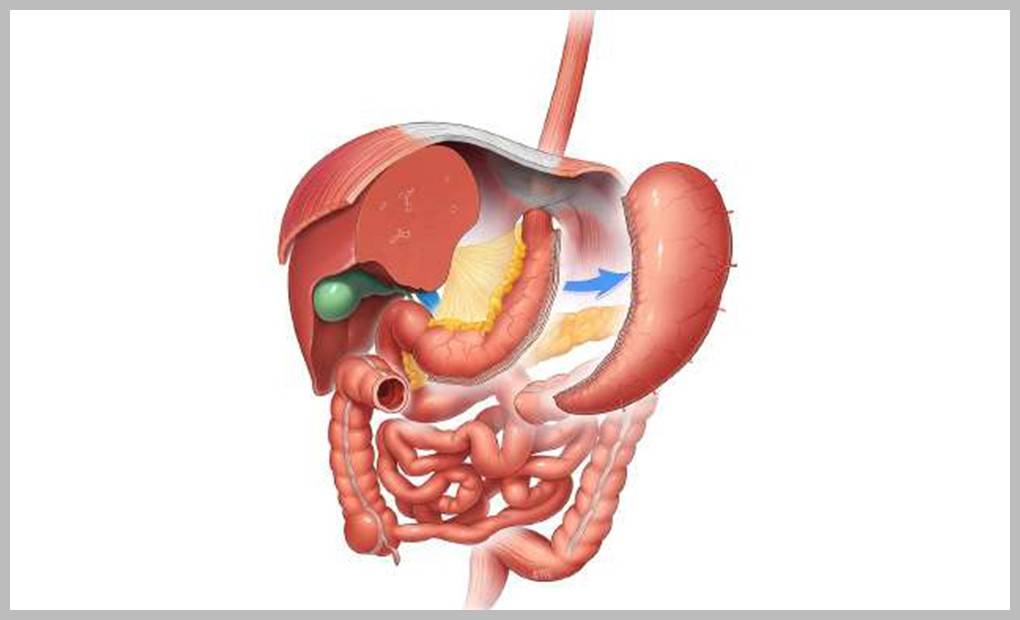
Laparoscopic Mini-Gastric Bypass (MGB-OAGB)
-
-
-
- Also known as One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass.
- It is a minimally invasive and reversible procedure performed with laparoscopic technique.
- It has a shorter operating time and lesser operative complication.
- This is an appropriate procedure for patients with a sweet tooth.
- It is beneficial for patients who suffer from obesity along with obesity-related disease(s).
- A small banana-like tube is separated from the stomach; this restricts the quantity of food intake. Unlike sleeve gastrectomy, the remaining portion of the stomach is not removed and remains inside the body. Then the small intestine is measured. A point, 150 to 250cm from the stomach is selected and then a joint is made with the banana-like tube. So the food passes through to the small intestine directly, bypassing the stomach and duodenum. Hence, the name Gastric Bypass.
- It has a shorter operating time and lesser operative complications.
- Patients are required to take life-long vitamin supplements and yearly blood tests after the surgery.
-
-
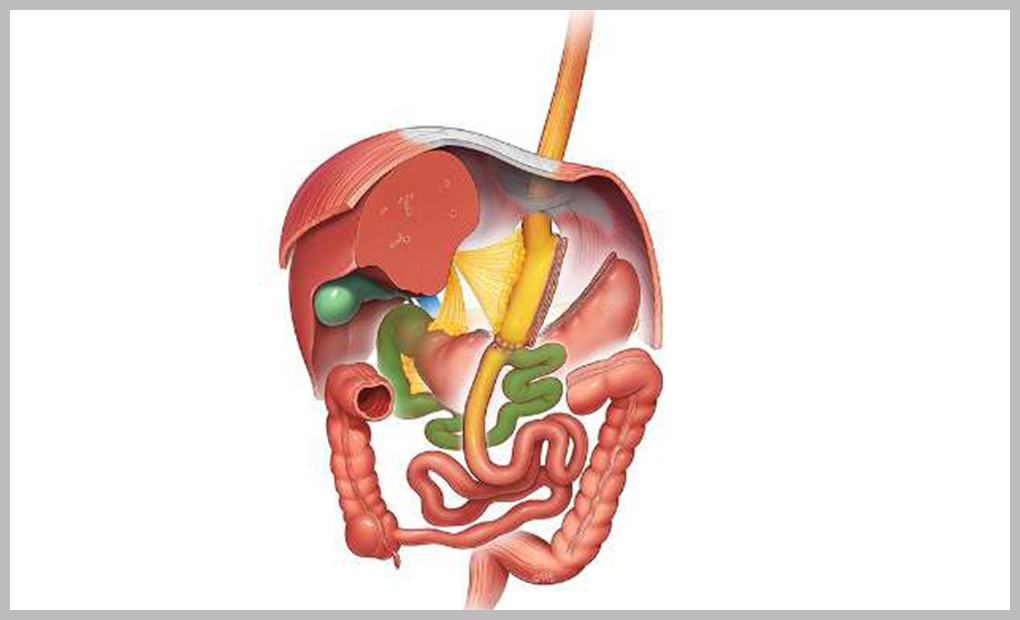
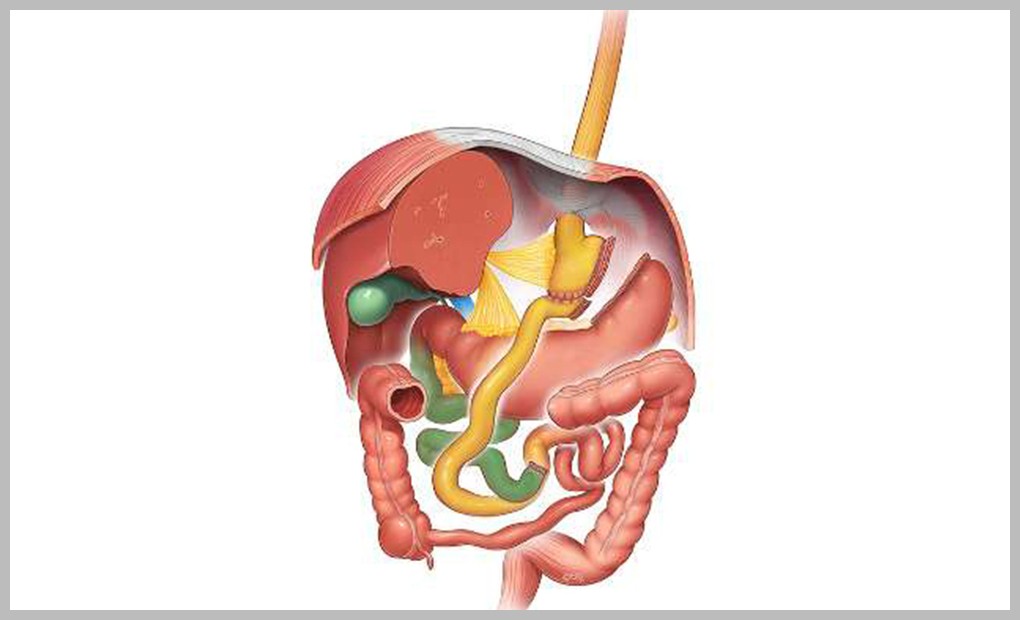
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: (RYGB)
-
-
- This is a reversible procedure.
- A small stomach pouch, approximately 30ml in volume is cut out from the upper end of the stomach. The first portion of the small intestine is divided, and the bottom end of the divided intestine is attached to the stomach pouch. The top portion of the divided small intestine is connected to the intestine further down. Hence, two joints/unions are made in comparison to the Mini Gastric Bypass.
- Patients are required to take life-long vitamin supplements and yearly blood tests after surgery.
-
Preparation for Surgery
Step 1 :
A detailed consultation with Dr. Tanvir will be scheduled to assess if you meet the eligibility criteria. The following areas will be thoroughly evaluated and discussed:
-
-
- Eating habits & weight history
- History of medical conditions and previous operations
- Current intake of medications
- History of mental health conditions
- Your age
- Rationale for bariatric surgery
- Your family history and support
-
Step 2:
If eligible, laboratory tests, x-rays, and ultrasounds will be prescribed. It is mandatory to have controlled diabetes and blood pressure before the operation. A consultation with a diabetologist, dietician and/or psychologist will be prescribed, if required.
Step 3:
The patient’s reports will be analyzed. An interactive Q&A and information session will be held to address any questions or concerns of the patient and his/her loved ones. The potential risks and complications of the operation will be discussed in detail.
The patient will be asked to speak/meet with former patients to learn about their experience and get a clearer perspective.
The patient will be provided with comprehensive instructions on how to prepare in the weeks before the surgery.
These instructions include:
-
-
- Preoperative nutritional diet
- Starting an exercise program
- Increasing water intake
- Breathing exercise/incentive spirometry
-
Step 4:
Once everything is clearly understood, the operation will be scheduled.
Life After Surgery
-
- Imagine being able to climb a flight of stairs without losing your breath or going shopping and finding your size or not having to struggle to fit into an airplane seat. Imagine simple tasks like effortlessly playing with your kid at the playground or having fun working out because there won’t be as much pressure on your joints or not having to spend as much on health care because you won’t need expensive prescription medication. For starters, simply by shedding 5-10% of your weight, you will have:
- increased energy levels & stamina
- lowered cholesterol & blood sugar levels
- reduced blood pressure
- reduced body aches & joint pain
- improved mobility
- improved breathing
- improved sleep
- prevented or potentially cured type 2 diabetes
- alleviated the need for some medications
- decreased the risk of erectile dysfunction
- improved physical appearance
- elevated self-esteem
- improved heart health
- relief from depression
- improved fertility
- treated PCOS symptoms
- reduced the risk of premature death by 30 to 40%
While bariatric surgery is the most efficient and long-lasting solution for people suffering from obesity and related diseases, to reap the numerous life-changing benefits of weight-loss surgery, the patient needs to commit to a healthy lifestyle, attend follow-up appointments, and thoroughly follow the doctor’s and dietitian’s instructions.
These instructions include:
- Post-operative nutritional guidelines
- Multivitamins, mineral & protein supplements
- Walking every day
- Continuing an exercise regimen
- Joining a weight loss support group
- Getting regular blood tests
- Imagine being able to climb a flight of stairs without losing your breath or going shopping and finding your size or not having to struggle to fit into an airplane seat. Imagine simple tasks like effortlessly playing with your kid at the playground or having fun working out because there won’t be as much pressure on your joints or not having to spend as much on health care because you won’t need expensive prescription medication. For starters, simply by shedding 5-10% of your weight, you will have: